Carbon
Carbon:

Image of two allotropes of carbon: diamond and graphite, respectively. The difference in their crystal structures controls their properties, hence why diamonds and graphite exhibit different physical properties.
Facts about Carbon:
- Carbon: Carbon is a solid that is transparent as diamond and black as graphite. Diamond is hard and has low conductivity; however, graphite is soft and is a good conductor.
- Fun fact about Carbon: Carbon appears in different forms, such as soot, coal, graphite, and diamond. It also is the main element of life, making up about 18% of the human body!
- Chemical symbol: C
- Atomic number: 6
A crystal structure containing Carbon:
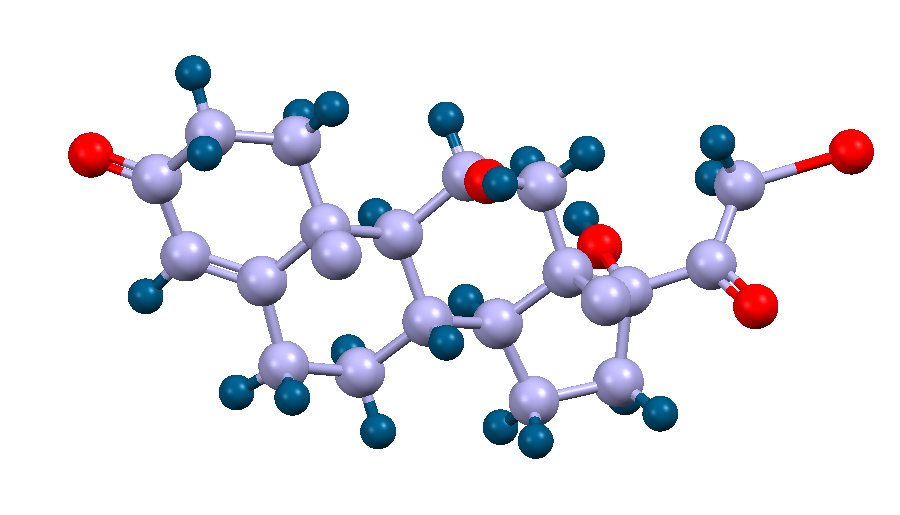
Crystal structure of a steroid hormone, cortisol. The carbon and hydrogen atoms are displayed as purple and blue spheres respectively.
Facts about this structure:
- Formula: C21 H30 O5
- Structure name: 11β,17α,21-Trihydroxy-pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione
- Fun fact about the structure: Cortisol is released during times of stress to prepare for the fight-or-flight response. It also performs other bodily functions, such as regulating blood pressure and reducing inflammation.
- CSD refcode: CORTSL (What’s this?)
- Associated publication: E.E.Castellano, P.Main, E.Westbrook, Acta Crystallographica,Section B:Struct.Crystallogr.Cryst.Chem., 1980, 36, 3063, DOI: 10.1107/S0567740880010801
More about Carbon:
Carbon is the sixth most abundant element, with three naturally occurring isotopes. Carbon-14 is a radioactive isotope that is found in all living tissues. Because of this, by measuring the amount of carbon-14 present in an object, the age can be determined. Carbon is also found in carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide. Carbon dioxide is a molecule that is absorbed by plants in photosynthesis and, as a solid, is also known as “dry ice”, which is known best as an example of sublimation. Carbon monoxide is a poisonous, colorless, and odorless gas that kills by binding itself to hemoglobin and suffocating tissues. Carbon is such a crucial part of life that there is an entire field of chemistry, organic chemistry, dedicated to the study of carbon and carbon-containing compounds, structures, and their reactions.
Learn More About the International Year of the Periodic Table (IYPT) in Crystals Project:
This project (#IYPTCrystals) is part of the International Year of the Periodic Table celebration (#IYPT2019), read more about the project here.
You can follow us on social media; search for #IYPTCrystals or follow The CCDC on X @ccdc_cambridge on Facebook ccdc.cambridge, on Instagram ccdc_cambridge or on YouTube CCDCCambridge.
Understand some of the terms and concepts used with our Frequently Asked Questions page here.
A 3D visualization showing Carbon in real crystal structures: