Scandium
Scandium:

Image of Scandium ore
Facts about Scandium:
- Scandium: Scandium is silvery white in colour and reacts with air and water.
- Fun fact about Scandium: Aluminium-Scandium alloys is used for sports equipment that needs to be strong and light weight. Such as bicycle frames, fishing rods, golf iron shafts and baseball bats.
- Chemical symbol: Sc
- Atomic number: 44.96
A crystal structure containing Scandium:
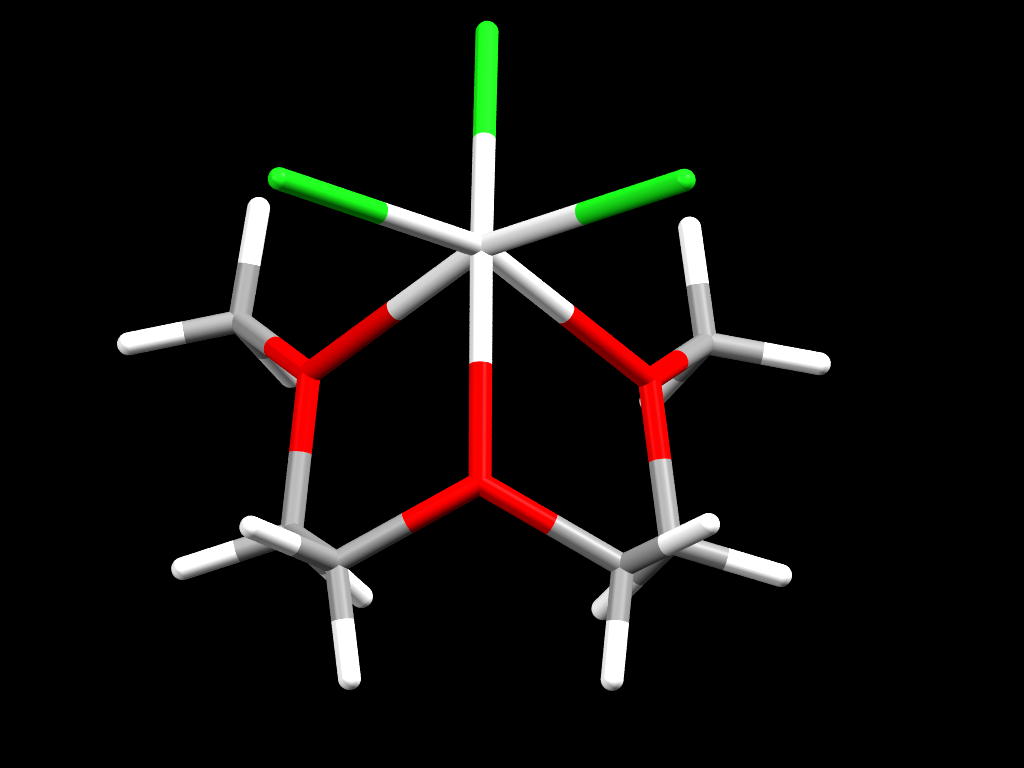
Structure of a hexa-coordinated colourless complex of Scandium 3+ ions
Facts about this structure:
- Formula: C6 H14 Cl3 O3 Sc
- Structure name: Trichloro-(2,5,8-trioxononane)-scandium
- Fun fact about the structure: This is a hexacoordinated Scandium complex. Even though Scandium is a member of the 3D block of elements this crystal is colorless, as most Scandium complexes are.
- CSD refcode: CORNIG (What’s this?)
- Associated publication: V.Ripert, L.G.Hubert-Pfalzgraf, J.Vaissermann, Polyhedron, 1999, 18, 1845, DOI: 10.1016/S0277-5387(99)00063-7
More about Scandium:
Scandium is the first member of the 3D block elements and the first rare earth elements. Scandium exhibits +3 oxidation state. In Sc3+ state, it has a completely empty 3D sub-shell. For this reason, generally Scandium complexes are colourless. Scandium is also not a transition metal in the true sense since it cannot exist in wide variety of transition states. Scandium has also no known biological role and is a suspected carcinogen.
Learn More About the International Year of the Periodic Table (IYPT) in Crystals Project:
This project (#IYPTCrystals) is part of the International Year of the Periodic Table celebration (#IYPT2019), read more about the project here.
You can follow us on social media; search for #IYPTCrystals or follow The CCDC on X @ccdc_cambridge on Facebook ccdc.cambridge, on Instagram ccdc_cambridge or on YouTube CCDCCambridge.
Understand some of the terms and concepts used with our Frequently Asked Questions page here.
A 3D visualization showing Scandium in real crystal structures: