Titanium
Titanium:
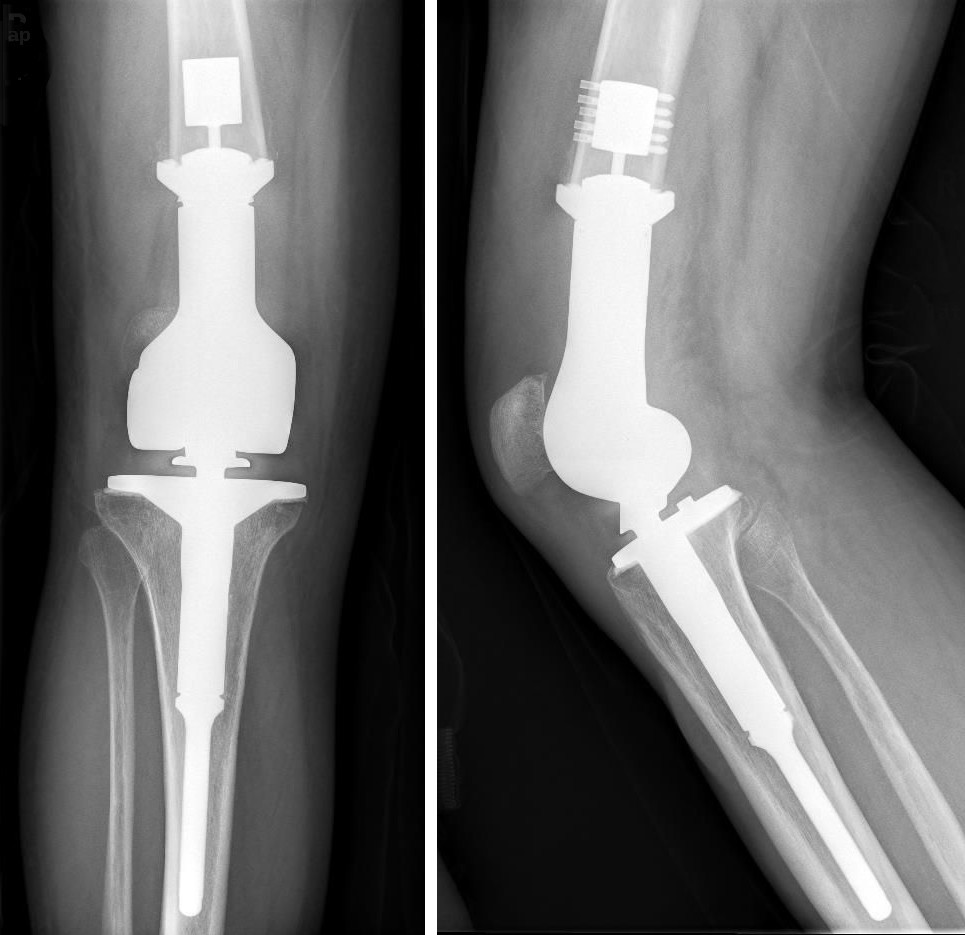
An X-ray of titanium knee replacement. Titanium does not react with the human body, so is often used in medical implants, including joint replacement and dentistry.
Facts about Titanium:
- Titanium: Silver solid at room temperature
- Fun fact about Titanium: Titanium implants can bond to bone, which improves the stability of the implant. This is known as osseointegration.
- Chemical symbol: Ti
- Atomic number: 22
A crystal structure containing Titanium:

Image showing a molecule of a Titanium-containing compound, known as Titanocene Y.
Facts about this structure:
- Formula: C26 H26 Cl2 O2 Ti
- Structure name: Dichloro-bis(η5-(p-methoxybenzyl)cyclopentadienyl)-titanium(iv)
- Fun fact about the structure: A number of Titanium-containing compounds, including this structure, have been investigated as potential anti-cancer drugs. Another Titanium compound, titanocene dichloride (CSD refcode: CDCPTI), was the first non-platinum coordination complex to undergo a clincal trial.
- CSD refcode: SECJAM (What’s this?)
- Associated publication: N.J.Sweeney, O.Mendoza, H.Muller-Bunz, C.Pampillon, F.-J.K.Rehmann, K.Strohfeldt, M.Tacke, J.Organomet.Chem., 2005, 690, 4537, DOI: 10.1016/j.jorganchem.2005.06.039
More about Titanium:
First discovered in 1791, Titanium was named after the Titans from Greek mythology. Titanium has a vast number of uses across a wide range of different areas including in medicine, jewellery, manufacturing and the chemical industry. Titanium is a very strong and lightweight metal and is often combined with other metals to form alloys. Important parts in lots of different vehicles, including aeroplanes and spacecraft, are made out of Titanium alloys. Compounds containing Titanium also have a wide range of applications. Titanium dioxide (TiO2) is commonly used as a white pigment in products such as toothpaste, paint and plastics. It is also added to some sunscreens to absorb harmful UV radiation. Titanium nitrides and carbides are extremely hard – thin layers of these materials are applied to the outside of cutting tools and drill bits to protect them. Titanium-containing compounds are also used as catalysts to help speed up chemical reactions. In 1963, the Nobel prize for Chemistry was awarded to Karl Ziegler and Giulio Natta for their work involving Titanium-containing catalysts.
Learn More About the International Year of the Periodic Table (IYPT) in Crystals Project:
This project (#IYPTCrystals) is part of the International Year of the Periodic Table celebration (#IYPT2019), read more about the project here.
You can follow us on social media; search for #IYPTCrystals or follow The CCDC on X @ccdc_cambridge on Facebook ccdc.cambridge, on Instagram ccdc_cambridge or on YouTube CCDCCambridge.
Understand some of the terms and concepts used with our Frequently Asked Questions page here.
A 3D visualization showing Titanium in a real crystal structure: