Ensemble Protein–Ligand Docking – Your Questions Answered
Protein–Ligand docking is an efficient strategy to identify bioactive conformations. It identifies possible compounds that bound to a specific target of interest and quickly screens the library of compounds. Many docking programs have been developed and applied in drug discovery. However, protein flexibility provides a challenge.
Ensemble docking overcomes this challenge by accounting for several discrete protein conformations for docking. The technique uses multiple conformations for a specific target.
A recent workshop focussed on performing ensemble docking using the protein–ligand docking software GOLD and the structure visualization software Hermes.
The interactive session sparked lively debate as examples were presented and exercises worked through by the participants who were guided by our drug discovery and cheminformatics scientists.
Here are some of the questions and answers from the workshop that we thought would benefit all by sharing.
Can You Calculate Binding Energy from Docking Results?
This is difficult. A docking score is a representation of how well a given ligand will bind to a protein, but docking scores are only crude estimates of binding affinity which contains many elements beyond the enthalpy of binding of a given ligand to a given protein.
Can You Remove Water from the Active Site?
You can remove water molecules from the active site as well as from other areas of the crystal structure.
What Happens If I Replace a Ligand with Another?
You can dock any other ligand in the binding site following the docking protocol.
How do I Link Databases for the GOLD Docking?
Download the database and use it as input. Note that GOLD needs a 3D structure of the ligands. If the library is in SMARTS we recommend using the CSD Python API (or RDKit) to convert SMARTS patterns to 3D structures.
How are GOLD Results Presented?
The GOLD ‘best_ranking.lst’ file contains the scoring terms for the ‘best’ pose along with the name of the molecule docked.
What Is the Minimum Limit for a Protein-Ligand Interaction?
When you perform the docking experiment the ligands bind to the active/binding site in the target protein. If the docked ligand forms interactions such as hydrogen bonds, pi–pi interactions, and/or fits in the binding site with structural similarity, then you may say that a protein–ligand interaction exists and the scoring functions give the docking score which helps rank the bond ligands.
Are the Hydrogens Added according to the Physiologic pH?
No. In GOLD hydrogens are added to each atom to satisfy the atom’s unfilled valencies, not based on pH.
In GOLD Is the Binding Site of the Protein Automatically Defined? Do I Need to Specify Any Values?
Gold allows you to define the binding site, there are four different options for selecting a binding site.
What Would Be the Approach If the Active Site or Binding Site for the Ligand in the Protein Is Unknown?
Blind docking with GOLD is possible but not recommended. I would use an alternative tool personally first (such as the fragment hotspots tool that uses the CSD – or SuperStar) to first probe the protein and analyse likely binding sites.
What Is the Maximum Value of PLP Fitness? Does That Number Indicate the Binding Affinity of the Ligand to the Protein?
If a ligand can occupy >1 tautomeric state we’d recommend docking both. GOLD doesn’t vary tautomers or protonation states. Scoring functions are fast approximate mathematical methods used to predict the strength of the interaction between two or more molecules. They are composed by several energy terms that contribute to the overall score. Find out more in the GOLD User Guide.
Is There a Way to Show Only the Best Ranked Pose in a Docking with Multiple Ligands?
Yes, it is possible to show the best ranked pose along with other solutions. Select the multiple solutions from the docking solution tab then, in the molecular explorer window, chose the display option to hide the protein residues and keep a single or reference protein. You may also change the style and colour.
How Can the Spin State of Water Molecules be Determined?
GOLD can include waters in the binding site in ‘toggle’ mode, ‘spin’ mode or ‘toggle and spin’ mode – so you can let the docking algorithm do it for you.
What Does GOLD Stand For?
GOLD is an acronym for Genetic Optimisation for Ligand Docking and is based on a genetic algorithm for docking flexible ligands into protein binding sites.
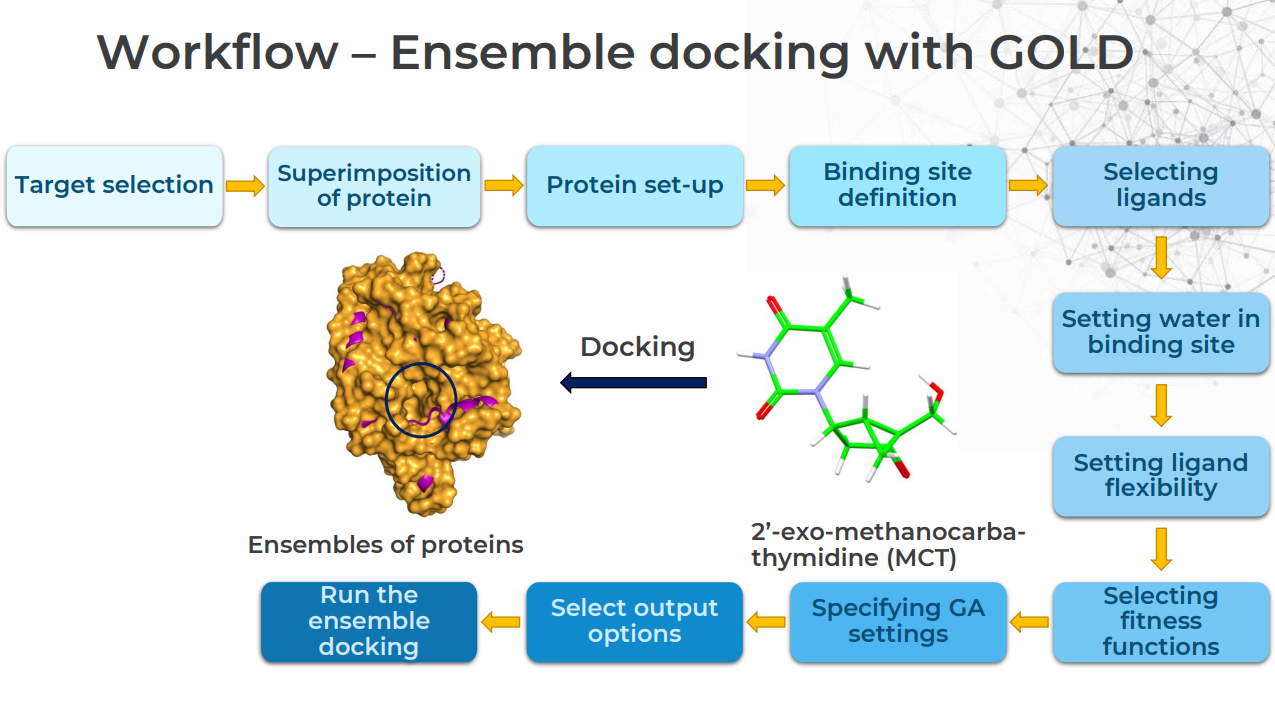
What Is a Typical Ensemble Docking Workflow in GOLD?
This is best answered graphically:
What Can I Do with the Protein Visualization Software Hermes?
Hermes is a structure visualization tool that enables users to visualize and edit macromolecules in 3D including proteins, nucleic acids, antibodies, and ligands. More information can be found here.
Do You Provide Any Protein–Ligand Docking Educational Resources for Remote Learning?
We provided on-demand modules to learn how to use the CCDC software at your own pace, including a certificate up completion. Start learning now.
I Heard a Rumour You Have a Protein–Ligand Docking Card Game?
That’s correct! Get your copy of Bound! A Protein–Drug Binding Game from our website.

Next Steps
Learn more about the protein–ligand docking software GOLD.